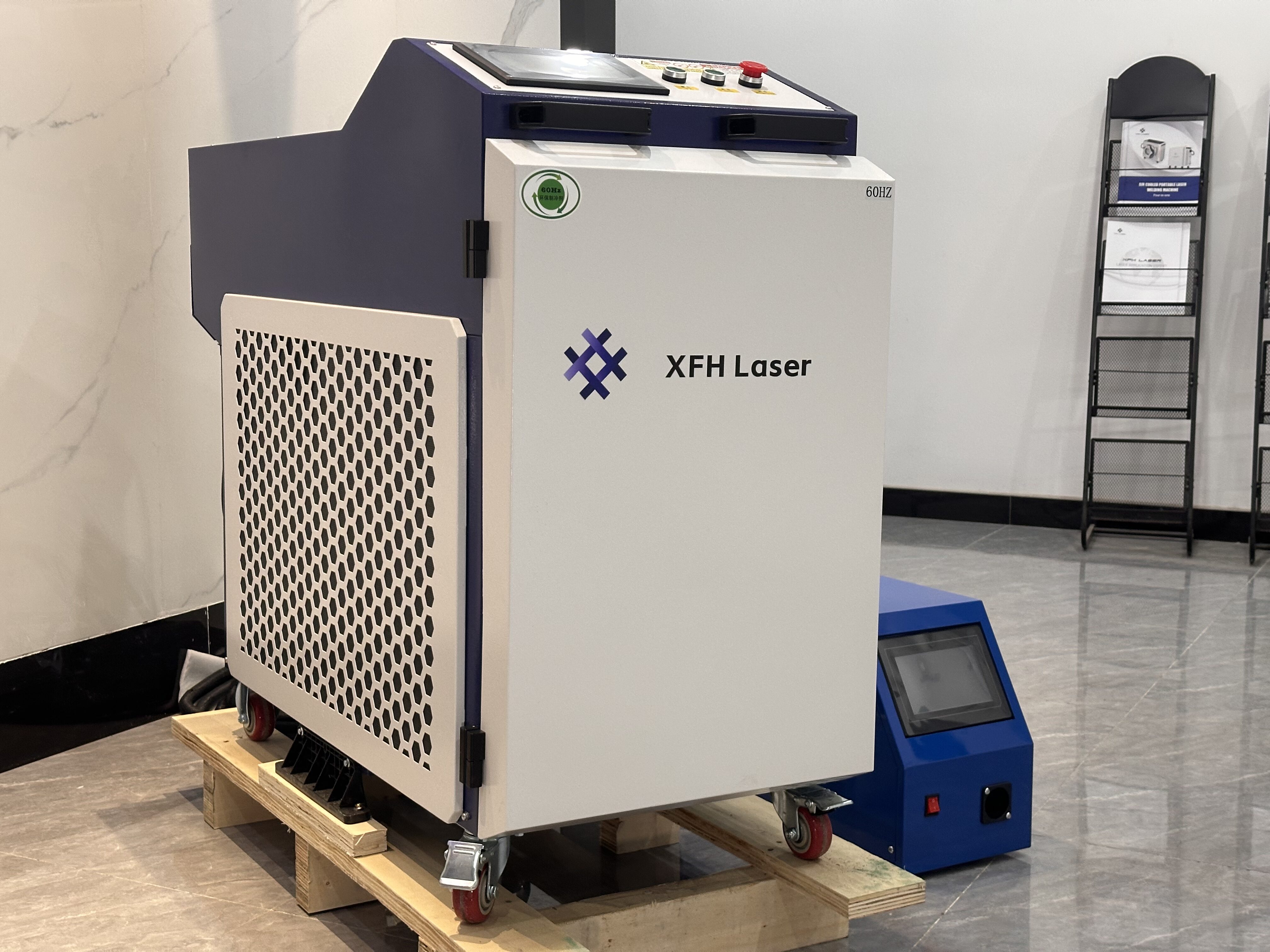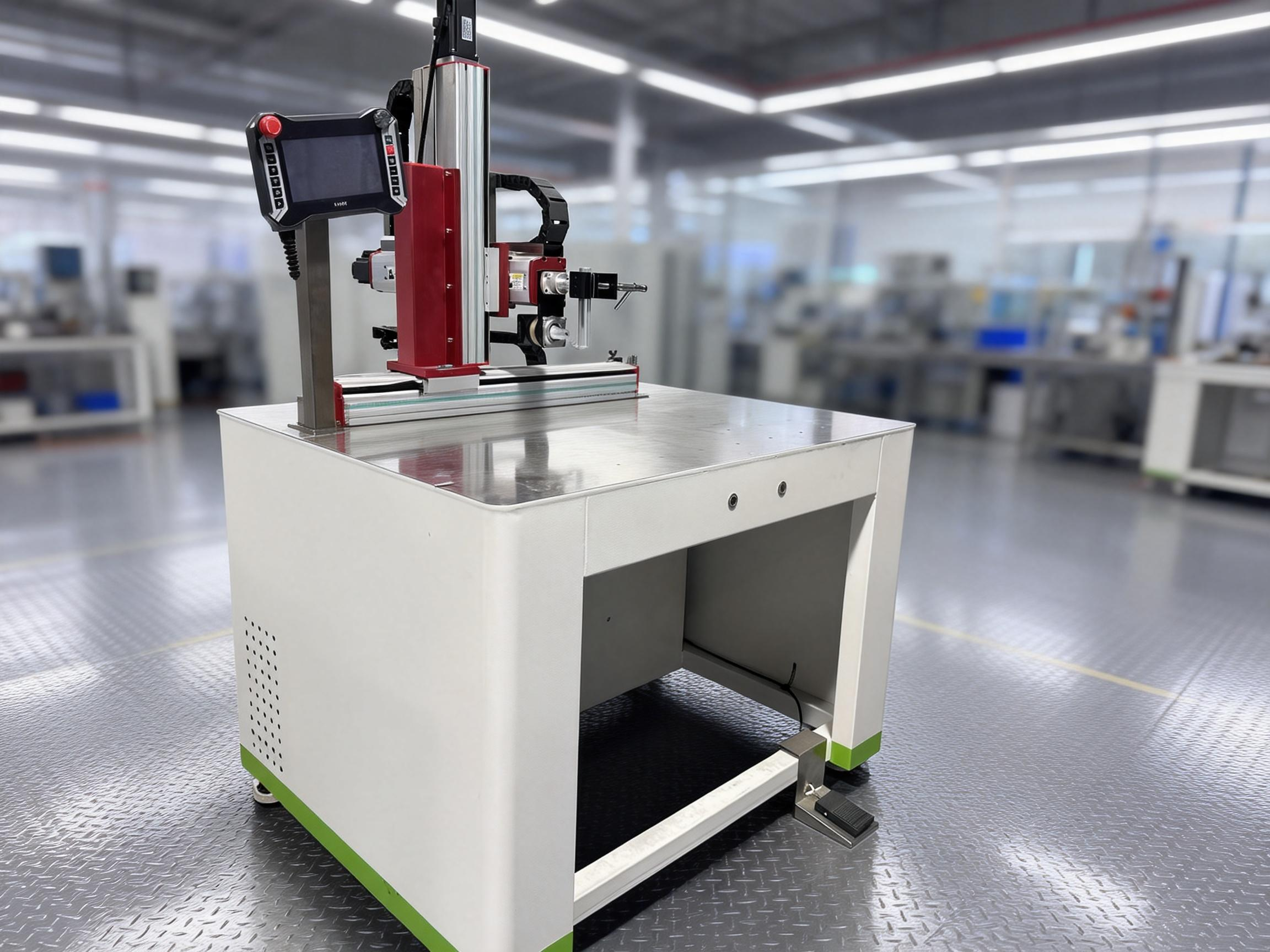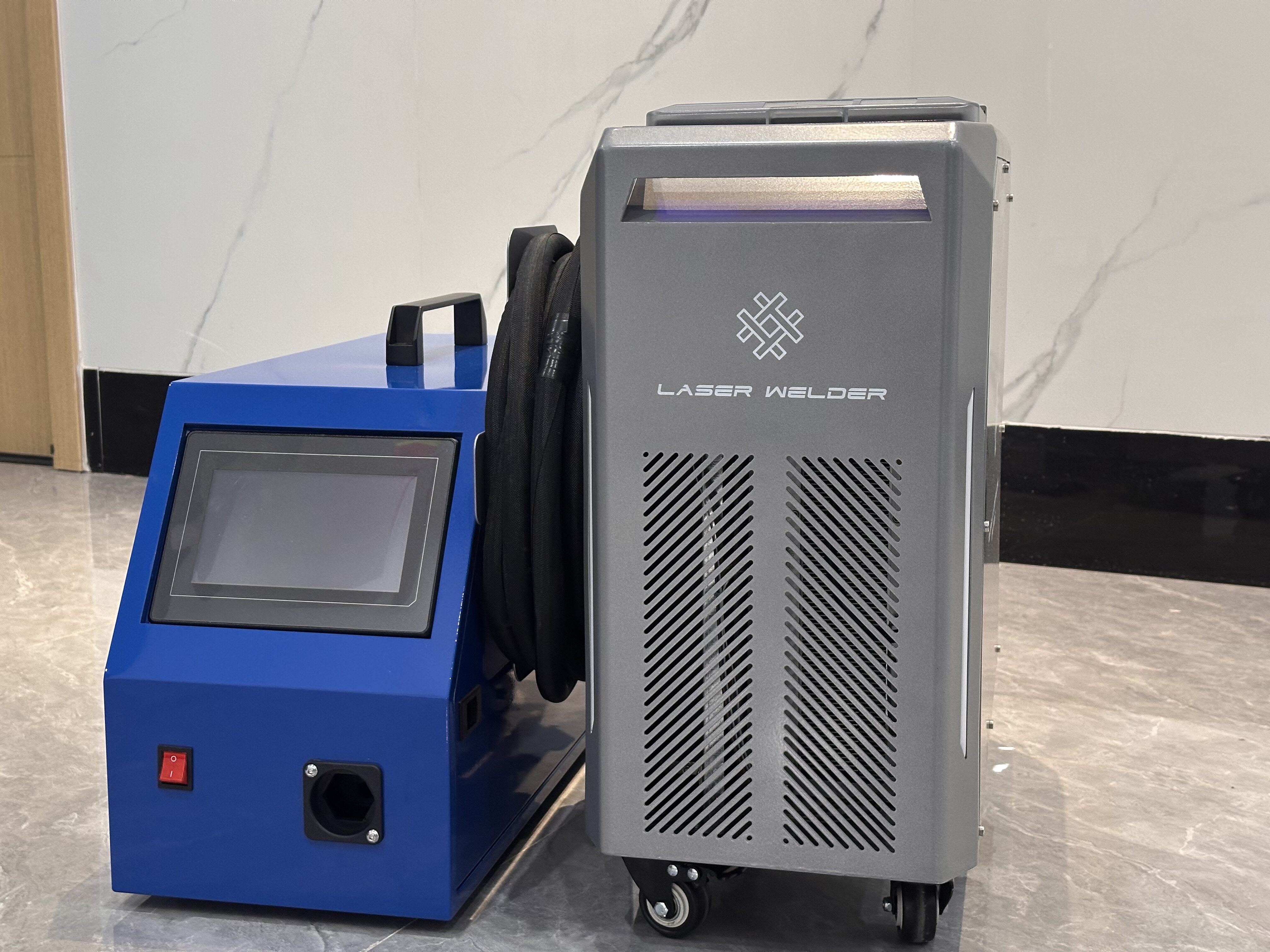



Battery laser welding machine
Laser System
-
Laser Type: Fiber laser
-
Laser Wavelength: 1064 nm
-
Laser Operation Mode: Continuous / Pulse (optional)
-
Output Power Options: 1000W / 1500W / 2000W / 3000W
-
Power Stability: ≤ ±1%
-
Beam Quality (M²): ≤ 1.3
-
Cooling Method: Water cooling
Welding Performance
-
Welding Speed: Up to 100–120 mm/s (depending on material and thickness)
-
Welding Thickness Range:
-
Battery tabs (Cu / Al / Ni): 0.1 – 1.5 mm
-
Busbars (Copper / Aluminum): up to 3.0 mm
-
-
Spot Diameter: 0.2 – 1.0 mm (adjustable)
-
Repeat Position Accuracy: ±0.02 mm
-
Energy Control Accuracy: ≤ ±2%
Motion & Control
-
Positioning System: Precision linear motor / servo motor
-
Control System: Industrial PC + motion control card
-
Programming Method: Teaching / CAD import (optional)
-
Vision System: CCD camera (optional)
Category:Laser welder
Product Details
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most important factor when choosing a laser welder?
The two most important factors are material thickness and usage scenario. Material thickness determines the required laser power, while the application scenario determines whether you need a handheld, workstation, or automated laser welding system.
2. How does material thickness affect laser welder selection?
Laser power must match the thickness of the material to ensure proper penetration and weld strength.
- 0.5–3 mm: Low to medium power laser welders are suitable for thin sheet metal and precision parts.
- 3–6 mm: Medium power laser welders are ideal for general fabrication and industrial components.
- 6 mm and above: High-power laser welders are recommended for structural parts and heavy-duty welding.
Choosing insufficient power may cause weak welds, while excessive power can lead to burn-through on thin materials.
3. Can one laser welder handle different thicknesses?
Yes. Most modern laser welders offer adjustable power settings, allowing them to handle a range of thicknesses. However, the base laser power should always be selected according to the most common thickness used in daily production.
4. How does the welding scenario influence the choice?
- Handheld laser welding: Best for flexible jobs, repairs, small batches, and irregular workpieces.
- Workshop or production welding: Suitable for repeated welding of standard parts with consistent thickness.
- Industrial or heavy-duty welding: Requires higher power, stable cooling, and often automated systems for continuous operation.
5. Does material type matter in addition to thickness?
Yes. Materials like stainless steel and carbon steel weld easily, while aluminum and copper reflect more laser energy and usually require higher power or optimized parameters, even at the same thickness.
6. Is higher laser power always better?
No. Higher power increases penetration but also raises cost and the risk of overheating thin materials. The best choice is a laser welder that matches your actual thickness range and application needs, not simply the highest wattage available.
7. What other features should I consider?
In addition to laser power, consider:
- Cooling system stability
- Welding head control and ergonomics
- Safety features and ease of operation
- Suitability for continuous or intermittent use
These factors directly affect long-term welding quality and productivity.
Summary
To choose the right laser welder, start with material thickness, then match it with your welding scenario. A properly selected laser welder delivers stable penetration, clean welds, and higher efficiency without unnecessary cost.
1. What is the first thing to consider when choosing a laser cleaning machine?
Start by identifying your cleaning needs: the type of material (metal, plastic, rubber), the kind of contaminants (rust, paint, oil), and the size of surfaces you will clean most often. Matching machine specs to these requirements is essential for effective cleaning.
2. How does laser power affect the choice?
Laser power determines how fast and effectively contaminants are removed:
- Low power (20–200W): Suitable for delicate surfaces, light rust, thin paint, or precision tasks.
- Medium power (200–500W): Ideal for general cleaning of rust, grease, and paint on moderate-sized parts.
- High power (500W+): Best for heavy-duty cleaning on thick coatings and large surfaces in industrial environments.
Choose the lowest power that safely handles your hardest cleaning task to avoid surface damage and excessive cost.
3. Should I choose handheld or stationary?
Handheld machines are great for flexible on-site cleaning, repairs, and variable workpieces. Stationary units or automated systems suit high-volume production, assembly lines, or fixed cleaning stations.
4. Is wavelength important?
Yes. The laser wavelength affects how well energy is absorbed by the material:
-
Fiber lasers (~1064 nm): Common for most metal cleaning.
-
CO₂ lasers (~10.6 µm): Often better for non-metal materials like plastics or wood.
Matching wavelength to material improves cleaning efficiency and reduces heat damage.
5. What about pulse type and frequency?
Laser cleaners can operate in pulsed or continuous modes:
-
Pulsed lasers: Deliver bursts of energy, reducing heat impact — ideal for precision cleaning and sensitive surfaces.
-
Continuous wave lasers: Provide steady output, useful for bulk contaminant removal where thermal impact is less critical.
Pulse frequency and duration influence how aggressively contaminants are removed without harming the substrate.
6. How does production volume influence my choice?
-
Small batches or occasional use: Compact or portable systems work best.
-
Continuous high throughput: Fixed or automated laser cleaning machines with robust cooling and duty cycles improve productivity.
Always consider how much cleaning your operation requires over time.
7. What safety and support features should I look for?
Ensure the machine has proper safety measures (interlocks, shielding), cooling systems to manage heat, and quality support from the supplier for training, maintenance, and repairs. Good safety design and after-sales service reduce risk and downtime.
8. Do I need to consider long-term costs?
Yes — look beyond the purchase price. Factor in operational costs like energy consumption, maintenance, consumables (filters, optics), and downtime costs. A machine that is inexpensive upfront but costly to maintain can reduce overall value.
9. Is testing important before buying?
Absolutely. Testing with your materials and contaminant types helps verify cleaning speed, power sufficiency, and surface impact. This practical step prevents mismatches between specifications and real-world performance.
10. What’s the best way to balance performance and cost?
Choose a machine that meets your heaviest cleaning need without over-specifying. For most general industrial tasks, a mid-range power laser cleaner (200–500W) balances cost, flexibility, and capability. For specialized tasks, adjust power, configuration, and automation accordingly.




